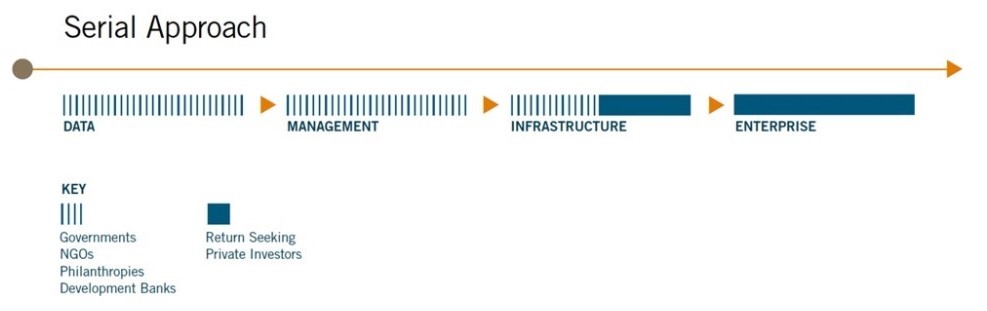
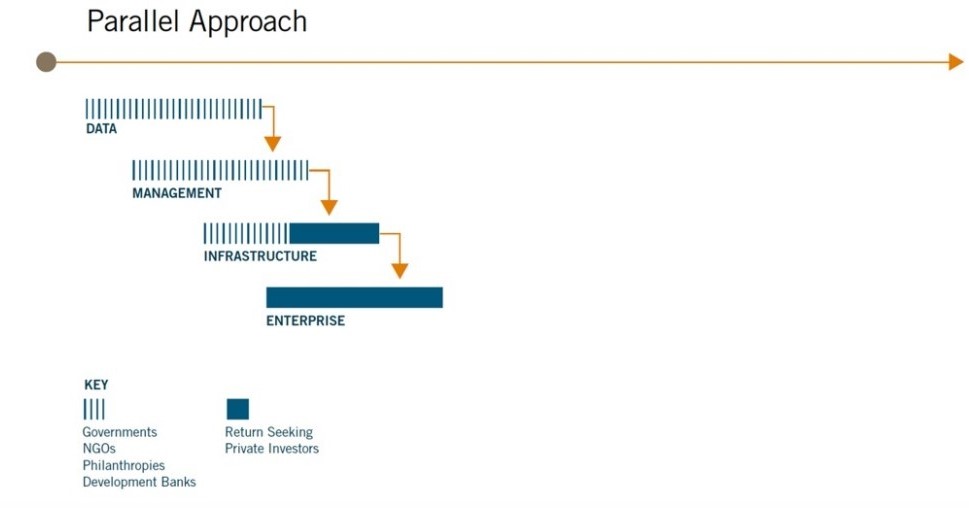
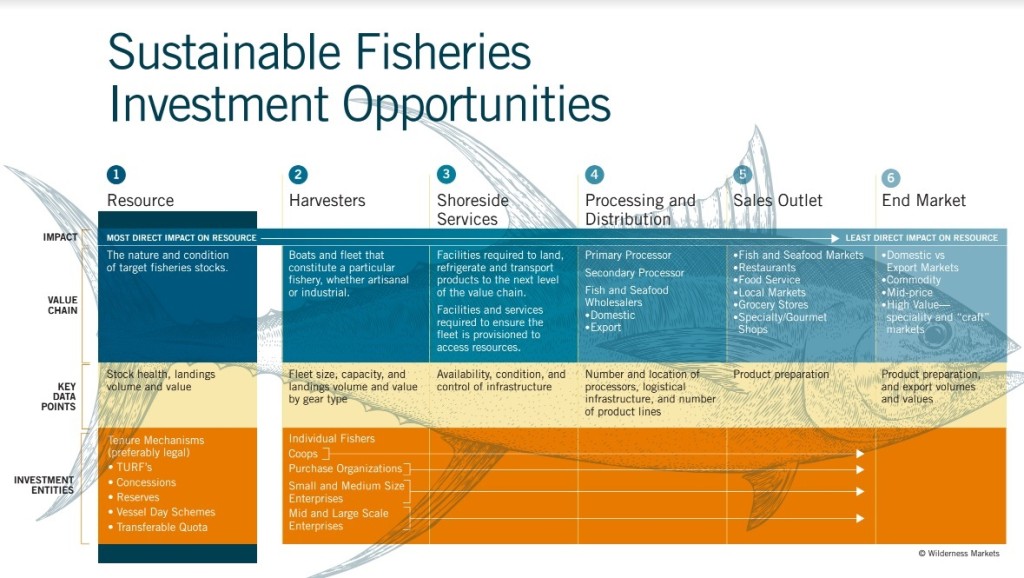
Improve Data to Improve Sustainability
Case Study:
Developing and Implementing SIMP Compatible Seafood Data Reporting and Traceability System in the Crab Supply Chain
Problem Statement and Opportunity
The U.S. implementation of the Seafood Import and Monitoring Program (SIMP)[1] on 1 January 2018 establishes reporting and recordkeeping requirements to prevent illegal, unreported and unregulated (IUU) seafood from entering the U.S. The onus of proof is placed on the importer of record to provide and report key data from harvest to U.S. entry. In geographically diffuse supply chains, like blue swimming crab from Southeast Asia, with thousands of “points of entry”, i.e., fishers, tracking landings to the vessel is far less straightforward than short and narrow supply chains, such as skipjack tuna or sardines. This reporting requirement, while worthwhile, will require U.S. seafood importers to incorporate cost-effective traceability initiatives in their often-complex supply chains.
There is a growing appreciation that the needs of fishers and their communities must be addressed in order to improve the underlying causes of fishery exploitation in the developing world, particularly for small-scale fisheries. -California Environmental Associates
The requirement also presents an opportunity to promote resource sustainability through supply chain transparency and catch monitoring. Despite pledges to abide by size limits, U.S. importers of blue swimming crab (BSC) have difficulty ensuring their supply chain partners are buying only crabs larger than the agreed minimum size of 10cm and excluding berried females. The application along with a web-based reporting tool we developed can meet the requirements of the SIMP, as well as the European Catch Documentation (CD) requirements, and elucidate the in-country supply chain. By tracking landings by vessel and by harvester, this tool further provides the opportunity to address key social and environmental outcomes associated with the Sustainable Development Goals[2] (SDGs), which gives seafood importers a mulit-purpose toolkit to both decrease their reporting costs and increase the sustainability of the crab stocks.
The opportunity to spur social and economic impact should not be underestimated. Educating, engaging and rewarding fishers and communities directly for complying with ecological goals like minimum size, berried females, no-take areas, and more offers an opportunity to engage communities directly in resource management and provide key links to SDGs. Aside from nascent work by Fair Trade[3] and SmartFish[4], there are few fishery sustainability efforts that actually benefit the fishers that form the foundation of many supply seafood chains. Indeed, most efforts impose costs on fishing communities—time, foregone income, capital for new equipment—without providing benefits. Our tool allows identification of compliant fishers, so they can be awarded price premiums and other incentives.
Supply chain transparency is beneficial to the U.S. importer not only in terms of identifying good actors and meeting reporting requirements, but also gives them an edge in the marketplace full of otherwise opaque supply chains.

Provision of ice is a key concern
Assessment
When initially considering how to provide BSC supply chain transparency from the ocean to the end buyer, we researched existing options, hoping to find one that could be customized to the supply chain. We conducted a desk review, scouring the internet and our personal network to identify all available options. In total, we reviewed nearly forty systems that provided varying levels of traceability; of these, we interviewed approximately six potential providers that met or came close to our key considerations:
- Ease of use – the user interface needed to be easy for data collectors in Indonesia and importers in the U.S. to use
- Utility for marketing purposes – a consumer-facing component was a must
- Facilitate regulatory compliance – must collect and provide data required by the SIMP and EU CD in a straightforward format
- Mapping – needs to provide maps of fishing locations to determine which areas are best for avoiding undersized and berried crabs
- Business model – a cost effective and durable business model that did not result in excessive fees or costs to each level of the value chain
- Data access, storage and ownership – data must be accessible by multiple parties within the value chain, stored in Indonesia, and owned by the funding company
- Reasonable set-up costs – ideally, a system would be compatible with existing software and hardware and would require little in the way of training. A team should be able to begin data collection with a few hours or less of upfront training on the system interface and they should be able to readily convey to the fishers the benefits of the system.
- Geographic and cultural relevance – the system needed to function in rural, relatively isolated areas with little to no telecommunications access
- Engage Harvesters and Vessel owners in order to build their understanding and the relative importance of adhering to harvest control regulation
- Ease of integration – overall, the platform needed to be easy to readily integrate into the supply chain.
Findings from Assessment
None of the reviewed systems met the requirements of the lead firm with the exception of the Pelagic Data Systems units for vessel management, i.e., vessel tracking. Due to the cost of acquisition and the relatively high ongoing costs of use, these were installed on a trial basis. This test was not successful, and cheaper, more effective units were identified.
Development
Not finding a suitable existing program, Blue Star Foods decided to develop their own application to gather data tied to their marketing goals and objectives around supply chain integrity. The SIMP and EU CD data requirements were integrated into the data collection system. Wilderness Markets worked closely with an app-development team to develop an Android and iOS application and support the field trials. After the initial field trials, the system was deployed to in-house teams from Blue Star Foods Indonesian partners, consisting of procurement and quality control specialists.
Implementation and Deployment
Data was collected at selected mini-plants and landing sites during a six-month period. Both harvesters and data collectors were simply encouraged to log landings during the pilot phase without any indication or reference to IUU or other considerations. They were not penalized or otherwise reprimanded for reporting undersized or berried crabs during this time period. Vessel tracking data was collected for a select number of boats during this period, which could be matched to landings data.

Sumatran Fisherman with Blue Swimming Crabs
Initial learning points
- Data collection required additional training of procurement and quality control teams. This in turn required an additional budget to be implemented effectively.
- The pilot only covered a small portion of overall U.S. imports from Indonesia (less than 1%) – the current opacity of the supply chain means we did not know how much each mini-plant contributes to the supply chain before the pilot
- The system efficiency is high enough that recording all landings at a mini-plant or at a landing site is possible, though unless a quality control individual is onsite continually, it cannot guarantee there will be no side selling unless all buyers agree to use the system.
- The data feedback loop to management has been significantly shortened and is possible in nearly real-time allowing:
- Faster identification of low productivity landing sites
- Faster identification of high productivity landing sites
- Faster identification of undersized and/or berried crab seasons and locations
- Data integrity and accuracy continues to be an issue and needs to be worked on – Due to their small size, most vessels are unregistered so vessel identification is challenging. Usual data integrity and accuracy issues for data collection operations exist, such as ensuring consistent data entry, checking entries for errors, etc.
Initial Data Findings
- Initial indications, based on sampling approximately 10% of the harvest per vessel, are that up to 25% of landings can likely be classified as IUU (berried females & sub 10cm).
- Boats with lowest supply chain loyalty appear to have higher levels of IUU (an assumption to be tested in additional sites)
- It is now possible to identify the specific boats that are causing the high levels of infractions, and to address with through the supply chain in a focused manner.
- Less than 20% of the surveyed vessels were responsible for 80% of the IUU landings
Fishery Management Implications
The ability to specifically identify vessels not complying with agreed harvest controls will permit a more targeted, focused and cost-effective approach to monitoring and enforcement of infractions. With less than 20% of the vessels are causing 80% of the issues with regards to IUU landings, efforts can be made to reduce IUU in a focused manner.
The data provides:
- Ability to provide shore-based landing information
- Ability to identify both geographic and seasonal potential closure options based on real data
- Ability to target enforcement based on recorded infractions

BSC fisherman with new vessel tracking device
Links to SDGs
In addition to the business and fishery management implications, the findings are directly linked to at least three SDGs:
SDG 8 Decent Work and Economic Growth
Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
Biological data indicates a quick (less than 1 year) stock recovery when undersized crabs are left in the water, thereby increasing the economic value of the fishery and decoupling growth from environmental degradation (Target 8.4)
SDG 9 Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation
Increasing the transparency of the supply chain means that small-scale enterprises, like the mini-plants, can have better access to financial services (Target 9.3).
SDG 14 Life Below Water
Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development
Using the data generated by the app, progress can be made towards sustainably managing fish stocks, combatting IUU, and providing meaningful market access for small-scale artisanal fishers (Targets 14.4, 14.6 and 14.B).
Recommendations and Next Steps
A key recommendation of the initial pilot is the need to establish unique vessel IDs with the support of local government authorities, which will allow more meaningful monitoring and enforcement of landings.
In addition, the need to engage with, and involve, other firms purchasing from the fishery was identified in order to reduce the opportunities for side selling.
A second phase is being planned to address the constraints of the first. The goal of the second phase is to:
- Capture a minimum of 25% of the Blue Star Foods Indonesia sourcing;
- Integrate improved vessel activity geographic data
- Expand geographically
- Include more processors, mini-plants and fishers in Indonesia, particularly in co-packer conditions
- Replicate into the Blue Star Foods Philippine supply chain
Conclusion
The drivers of market access compliance requirements, improved social and financial impact in in artisinal fisheries and greater supply chain integration are powerful drivers for change in any industry. The relatively low cost now associated with data capture tools mean lead firms can utilize almost ubiquitous cell phone availability to cost effectively assess the degree and extent of IUU in their supply chain, while strengthening their impact objectives and improving market recognition.
This approach provides resource managers and NGOs as well as development agencies with a relevant, cost effective tool to engage private sector supply chains in achieving SDGs in a measurable, informed and data driven manner.
[1] “U.S. Seafood Import Monitoring Program”. Retrieved on 7 March 2018 from: https://www.iuufishing.noaa.gov/RecommendationsandActions/RECOMMENDATION1415/FinalRuleTraceability.aspx
[2] “Sustainable Development Goals”. Retrieved on 19 March 2018 from https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/?menu=1300
[3] “Capture Fisheries Standard (CFS)”. Retrieved on 8 March 2018 from: https://www.fairtradecertified.org/business/producer-certification
[4] “Rescate de Valor”. (English: Value Rescue) Retrieved on 8 March 2018 from: http://rescatedevalor.org/